The PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) certification is a special title given to people who really have a solid understanding when it comes to business analysis. They’ve shown they can use these skills in real-life situations. This certification is given out by the Project Management Institute (PMI), a worldwide group that’s all about making project management top-notch.
PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) Exam Glossary
Here are some key terms and concepts that may appear on the PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) certification exam:
- Business Analysis: The practice of identifying business needs, analyzing problems, and developing solutions to address those needs and problems.
- Stakeholder: Any individual or group who has an interest in or will be affected by a business analysis initiative.
- Requirements: Statements of the needs or constraints of a stakeholder that must be met by a solution.
- Elicitation: Collecting and writing down what stakeholders need by talking to them in different ways, like interviews, surveys, and workshops.
- Analysis: The process of evaluating requirements to identify potential solutions and to determine the best approach for meeting stakeholder needs.
- Traceability: The ability to track requirements from their origin to the final solution, ensuring that all requirements have been met and any changes have been properly documented.
- Verification and Validation: The process of ensuring that requirements have been correctly interpreted, implemented, and tested, and that the resulting solution meets stakeholder needs.
- Change Control: The process of managing changes to requirements, ensuring that any changes are properly documented, evaluated, and approved.
- Agile: An iterative and incremental approach to project management that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
- Waterfall: A conventional step-by-step way of managing a project where you finish one part before starting the next.
PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) Exam Guide
Here are some official resources that can help you prepare for the PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) certification exam:
- PMI-PBA Handbook: This document provides an overview of the PMI-PBA certification, including eligibility requirements, the application process, and the exam content outline.https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/certifications/professional-in-business-analysis-handbook.pdf
- PMI-PBA Exam Content Outline: This document outlines the topics that are covered on the PMI-PBA certification exam. You can use this outline to guide your study and preparation for the exam. https://www.pmi.org/-/media/pmi/documents/public/pdf/certifications/professional-in-business-analysis-exam-content-outline.pdf
- PMI-PBA Exam Prep Course: PMI offers an online exam preparation course for the PMI-PBA certification. This course covers the exam content outline and provides practice questions to help you prepare for the exam. https://www.pmi.org/shop/p/pmi-professional-in-business-analysis-pba-exam-prep-online-course/16202
- PMI-PBA Practice Exam: PMI offers a practice exam for the PMI-PBA certification. This practice exam includes questions similar to those you will encounter on the actual exam and can help you assess your readiness for the certification.https://www.pmi.org/shop/p/pmi-professional-in-business-analysis-pba-practice-exam/16204
- PMI-PBA Study Group: PMI offers a study group for individuals preparing for the PMI-PBA certification. This study group provides a forum for candidates to ask questions, share knowledge, and receive support from other individuals preparing for the exam. https://www.pmi.org/membership/volunteer/volunteer-opportunities/pmi-pba-study-group
PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) Exam Tips and Tricks
Here are some tips and tricks to help you prepare for the PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) certification exam:
- Familiarize yourself with the exam content outline: The PMI-PBA exam content outline provides a detailed breakdown of the topics that will be covered on the exam. Make sure you are familiar with all of the topics and subtopics.
- Use multiple study resources: PMI offers a variety of study resources, including online courses, practice exams, and study groups. Consider using multiple resources to help you prepare for the exam and reinforce your understanding of key concepts.
- Practice time management: The PMI-PBA exam is timed, so it’s important to practice time management when studying and taking practice exams. Make sure you are comfortable with the pace at which you need to answer questions. Practice pacing yourself to ensure you have enough time to answer all of the questions on the exam.
- Pay attention to key words: The PMI-PBA exam may use key words such as “most likely” or “least likely” in questions, so it’s important to pay attention to these key words and understand what they are asking for.
- Take breaks and stay focused: The PMI-PBA exam is a lengthy and challenging exam. It’s important to take breaks and stay focused throughout the exam. Take breaks when needed to rest and refocus, and make sure you are fully focused and alert when answering questions.
- Stay confident and positive: Finally, it’s important to stay confident and positive throughout the exam. Believe in yourself and your abilities, and remember that you have prepared thoroughly for the exam.
PMI Professional In Business Analysis (PMI-PBA)® Course
The exam will have following major testing basis.Therefore, undertaking the following tasks will help to reach the goal –
Firstly, Needs Assessment 18%
| Task 1 | – Firstly, Define or review a business problem or opportunity using problem and opportunity analysis techniques in order to develop a solution scope statement and/or to provide input to create a business case. |
| Task 2 | – Collect and analyze information from a variety of sources using valuation tools and techniques to contribute to determining the value proposition of the initiative |
| Task 3 | – Also, Collaborate in the development of project goals and objectives by providing clarification of business needs and solution scope in order to align the product with the organization’s goals and objectives. |
| Task 4 | – Identify stakeholders by reviewing goals, objectives, and requirements in order that the appropriate parties are represented, informed and involved. |
| Task 5 | – Also, Determine stakeholder values regarding the product, using elicitation techniques in order to provide a baseline for prioritizing requirements. |
Secondly, Planning 22%
| Task 1 | – Firstly, , Review the business case, and the project goals and objectives, in order to provide context for business analysis activities. |
| Task 2 | – Secondly, Define strategy for requirements traceability using traceability tools and techniques in order to establish the level of traceability necessary to monitor and validate the requirements. |
| Task 3 | – Furthermore, Develop requirements management plan by identifying stakeholders, roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and methods for eliciting, analyzing, documenting, managing, and In addition, approving requirements in order to establish a roadmap for delivering the expected solution. |
| Task 4 | – Subsequently, Select methods for requirements change control by identifying channels for communicating requests and In addition, processes for managing changes in order to establish standard protocols for incorporation into the change management plan. |
| Task 5 | – Also, Select methods for document control by using documentation management tools and techniques in order to establish a standard for requirements traceability and versioning. |
| Task 6 | – Lastly, Define business metrics and acceptance criteria by collaborating with stakeholders for use in evaluating when the solution meets the requirements. |
Thirdly, Analysis 35%
| Task 1 | – Furthermore, Elicit or identify requirements, using individual and group elicitation techniques in order to discover and capture requirements with supporting details (e.g., origin and rationale). |
| Task 2 | – Secondly, Analyze, decompose, and elaborate requirements using techniques such as dependency analysis, interface analysis, and In addition, data and process modeling in order to collaboratively uncover and clarify product options and capabilities. |
| Task 3 | – Also, Evaluate product options and capabilities by using decision-making and valuation techniques in order to determine which requirements are accepted, deferred, or rejected. |
| Task 4 | – Allocate accepted or deferred requirements by balancing scope schedule, budget, and resource constraints with the value proposition using prioritization, dependency analysis, and decision-making tools and techniques in order to create a requirements baseline. |
| Task 5 | – Also, Obtain sign-off on requirements baseline using decision-making techniques in order to facilitate stakeholder consensus and achieve stakeholder approval. |
| Task 6 | – Subsequently, Write requirements specifications using process (such as use cases, user stories), data, and In addition, interface details in order to communicate requirements that are measurable and actionable (that is, suitable for development). |
| Task 7 | – Furthermore, Validate requirements using tools and techniques such as documentation review, also, prototypes, demos, and also, other validation methods in order to ensure requirements are complete, accurate and aligned with goals, objectives, and In addition, value proposition. |
| Task 8 | – Lastly, Elaborate and specify detailed metrics and acceptance criteria using measurement tools and techniques for use in evaluating whether the solution meets requirements. |
Fourthly, Traceability and Monitoring 15%
| Task 1 | – Firstly, Track requirements using a traceability artifact or tools, capturing the requirements’ status, sources and relationships (including dependencies), in order to provide evidence that the requirements are delivered as stated. |
| Task 2 | – Subsequently, Monitor requirements throughout their lifecycles using a traceability artifact or tool in order to ensure the appropriate supporting requirements artifacts (such as models, also, documentation, and test cases) are produced, reviewed and approved at each point in the lifecycle. |
| Task 3 | – Also, Update a requirement’s status as it moves through its life cycle states by communicating with appropriate stakeholders. In addition, recording changes in the traceability artifact or also, tool in order to track requirements towards closure. |
| Task 4 | – Furthermore, Communicate requirements status to project manager and other stakeholders using communication methods in order to keep them informed of requirements issues, also, conflicts, changes, also, risks, and overall status. |
| Task 5 | – Lastly, Manage changes to requirements by assessing impacts, dependencies, and risks in accordance with the change control plan, and comparing to the requirements baseline in order to maintain the integrity of the requirements, In addition, associated artifacts. |
Lastly, Evaluation 10%
| Task 1 | – Validate the solution’s test results, reports, and other test evidence against the requirements acceptance criteria in order to determine whether the solution satisfies the requirements. |
| Task 2 | – Further, Analyze and communicate the solution’s identified gaps and deltas using quality assurance tools. In addition, methods in order to enable stakeholders to resolve discrepancies between solution scope, also, requirements, and developed solution. |
| Task 3 | – Subsequently, Obtain stakeholder sign-off on the developed solution using decision-making techniques in order to proceed with deployment. |
| Task 4 | – Also, Evaluate the deployed solution using valuation techniques in order to determine how well the solution meets the business case and value proposition. |
So, now we are done with the syllabus details. We will now be moving on to the most important step for the preparation – Study guide and resources.
Learning Resources for PMI-PBA Exam
There are many materials you can use to get ready. However, it can be tough to pass the certification if you don’t pick the right ones. So, be cautious when choosing your materials because they will affect how well you do on the exam. Let’s take a look at a few helpful resources.
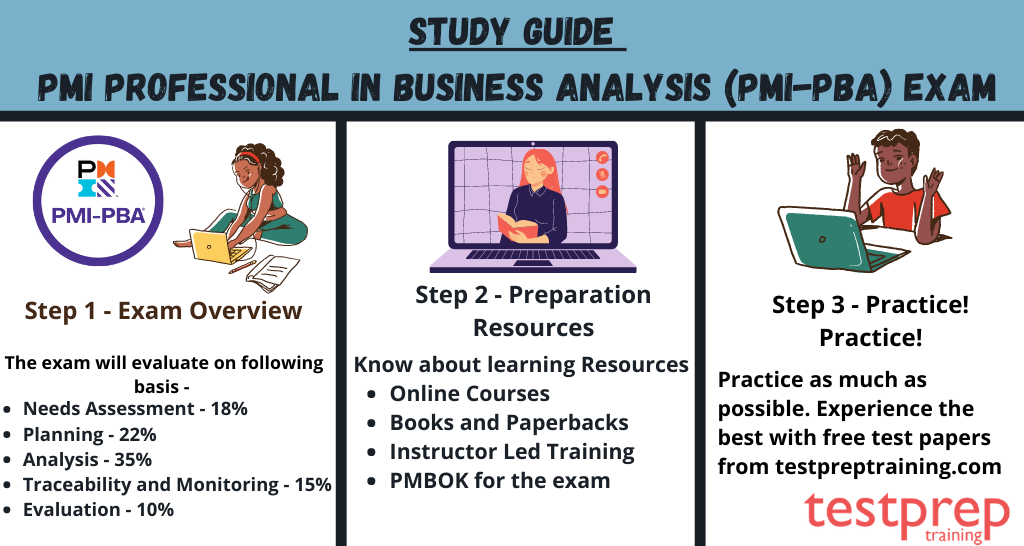
Resource 1 – Learn with Books and PMI Documentations

You’re free to use as many books as you like, which you can find at bookstores or libraries. Books are the best and dependable way to gather information about the theory part of the syllabus. Just make sure the books you choose cover all the topics that will be tested in the exam. Here are some PMI PBA Reference Books you can study with:
- Firstly, The PMI Guide to Business Analysis Paperback by Project Management Institute.
- Secondly, Business Analysis for Practitioners: A Practice Guide Paperback by Project Management Institute
- Thirdly, Achieve Business Analysis Certification: A Concise Guide to PMI-PBA®, CBAP® and CPRE Exam Success Pap/Psc Edition, by Klaus Nielsen
Resource 2 – Referring to online community
Online communities are made up of professionals in a certain field or people who are interested in the same area. So, don’t be shy about asking questions in these communities. You can also inquire about their study strategies or the resources they used to pass the exam. Additionally, you can check out online learning tutorials provided by Testpreptraining.com!
Resource 3 – PMI Training and Online Courses
You can also take advantage of PMI PBA Certification Online Training and web-based classes to understand the concepts better and build a strong foundation. Although the person taking the exam already has experience in project management and practical aspects, it’s important to now focus more on the theoretical aspect. This can be achieved through expert training or classes from a reputable organization.
PMI offers training programs for each exam, which include details about the exam, such as its description, target audience, how it’s delivered, and how long it takes. To prepare for the PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) exam, it’s advisable to enroll in one of these training programs to acquire the necessary knowledge and skills.

Resource 4 – Evaluation yourself with PMI PBA Practice Test
Furthermore, practice papers and test series are a great way to measure how well you’re doing. They assist you in pinpointing areas where your preparation needs improvement. Many trustworthy websites offer sample papers and test series, and some even provide free practice tests. Try a free practice test now! Make sure to practice as much as you can in order to reach the best level.



