Microsoft Intune app management
You can use Microsoft Intune as an IT administrator to manage the client apps that your employees utilize. In addition to managing devices and safeguarding data, this feature is available. Ensuring that end users have access to the apps they need to complete their jobs is one of an administrator’s top priorities. This aim may be difficult to achieve because:
- There is a wide range of device platforms and app types.
- You might need to manage apps on both company devices and users’ personal devices.
- You must ensure that your network and your data remain secure.
Mobile Application Management (MAM) basics
The suite of Intune management services that enables you to publish, push, configure, protect, monitor, and update mobile apps for your users is known as Intune mobile application management.
Within an application, MAM helps you to manage and safeguard your organization’s data. A business or school-related app containing sensitive data can be handled on nearly any device, including personal devices in bring-your-own-device (BYOD) settings, using MAM without enrollment (MAM-WE). Intune MAM can handle a variety of productivity programs, including Microsoft Office products. Check out the official list of Microsoft Intune-protected apps that are open to the public.
Intune MAM supports two configurations:
- Intune MDM + MAM: IT administrators can only manage apps using MAM and app protection policies on devices that are enrolled with Intune mobile device management (MDM). To manage apps using MDM + MAM, customers should use the Intune console in the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com.
- MAM without device enrollment: MAM without device enrollment, or MAM-WE, allows IT administrators to manage apps using MAM and app protection policies on devices not enrolled with Intune MDM. This means apps can be managed by Intune on devices enrolled with third-party EMM providers. To manage apps using MAM-WE, customers should use the Intune console in the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com. Also, apps can be managed by Intune on devices enrolled with third-party Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) providers or not enrolled with an MDM at all. For more information about BYOD and Microsoft’s EMS, see Technology decisions for enabling BYOD with Microsoft Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS).
Get started
You can find most app-related information in the Apps workload, which you can access by doing the following:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center.
- Select Apps.
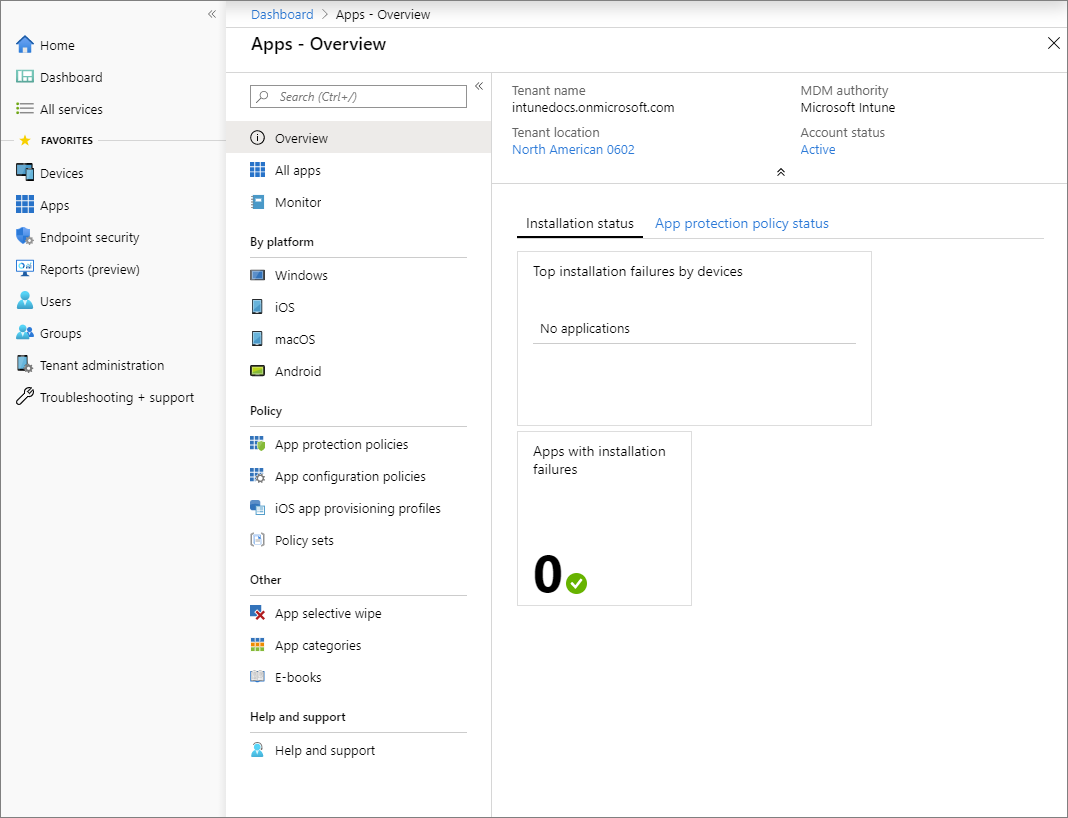
The apps workload provides links to access common app information and functionality.
The top of the App workload navigation menu provide commonly used app details:
Overview:
- Select this option to view the tenant name, the MDM authority, the tenant location, the account status, app installation status, and app protection policy status.
All apps:
- Select this option to display a list of all available apps. You can add additional apps from this page. Additionally, you can see the status of each app, as well as whether each app is assigned. For more information, see Add apps and Assign apps.
Monitor apps:
- App licenses: View, assign, and monitor volume-purchased apps from the app stores. For more information, see iOS volume-purchased program (VPP) apps and Microsoft Store for Business volume-purchased apps.
- Also, Discovered apps: View apps that were assigned by Intune or installed on a device. For more information, see Intune discovered apps.
- Subsequently, App install status: View the status of an app assignment that you created. For more information, see Monitor app information and assignments with Microsoft Intune.
- Furthermore, App protection status: View the status of an app protection policy for a user that you select.
By Platform:
- Select these platforms to view the available apps by platform.
- Firstly, Windows
- Also, iOS
- Furthermore, macOS
- Subsequently, Android
Policy:
- Firstly, App protection policies: Select this option to associate settings with an app and help protect the company data it uses. For example, you might restrict the capabilities of an app to communicate with other apps, or you might require the user to enter a PIN to access a company app.
- Also, App configuration policies: Select this option to supply settings that might be required when a user runs an app.
- Further, iOS app provisioning profiles: iOS apps include a provisioning profile and code that is signed by a certificate. When the certificate expires, the app can no longer be run. Intune gives you the tools to proactively assign a new provisioning profile policy to devices that have apps that are nearing expiration.
- Also, S mode supplemental policies: Select this option to authorize additional applications to run on your managed S mode devices.
- Finally, Policy sets: Select this option to create an assignable collection of apps, policies, and other management objects you’ve created.
Other:
- Firstly, App selective wipe: Select this option to remove only corporate data from a selected user’s device.
- Subsequently, App categories: Add, pin, and delete app category names.
- Furthermore, E-books: Some app stores give you the ability to purchase multiple licenses for an app or books that you want to use in your company.
- Help and support: Troubleshoot, request support, or view Intune status. For more information, see Troubleshoot problems.

Reference Documentation – What is Microsoft Intune app management?
