How to Initiate a storage account failover?
This guide will teach you how to use the Azure interface to start an account failover for your storage account. You can force an account failover if the primary endpoint for your geo-redundant storage account becomes unavailable for any reason. Your storage account’s secondary endpoint is updated to become the primary endpoint after an account failover. Clients can begin writing to the new primary region after the failover is complete. Forced failover allows you to keep your apps available at all times.
Prerequisites
Make sure your storage account is configured for geo-replication before performing an account failover. Any of the following redundancy options are available for your storage account:
- Firstly, Geo-redundant storage (GRS) or read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS)
- Also, Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS) or read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS)
How to Initiate the failover?
To initiate an account failover from the Azure portal, follow these steps:
- Firstly, Navigate to your storage account.
- Subsequently, Under Settings, select Geo-replication. The following image shows the geo-replication and failover status of a storage account.
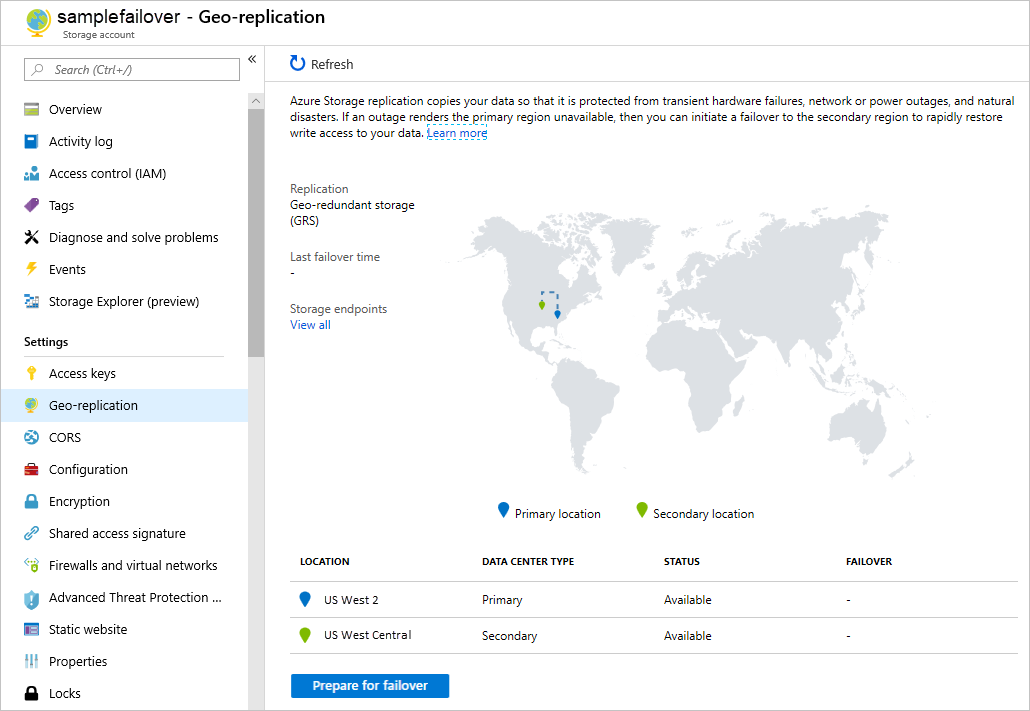
- Furthermore, Verify that your storage account is configured for geo-redundant storage (GRS) or read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS). If it’s not, then select Configuration under Settings to update your account to be geo-redundant.
- Also, The Last Sync Time property indicates how far the secondary is behind from the primary. Last Sync Time provides an estimate of the extent of data loss that you will experience after the failover is completed. For more information about checking the Last Sync Time property, see Check the Last Sync Time property for a storage account.
- Then, Select Prepare for failover.
- Finally, Review the confirmation dialog. When you are ready, enter Yes to confirm and initiate the failover.
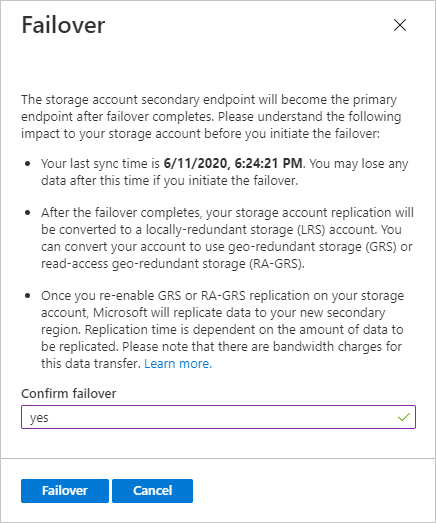
Know about Important implications of account failover
- The DNS records for the secondary endpoint are updated when you begin an account failover for your storage account, making the secondary endpoint the primary endpoint. Before you start a failover, make sure you understand the possible impact on your storage account.
- Check the Last Sync Time attribute to determine the level of anticipated data loss before initiating a failover. However, the time it takes to failover after initiation varies, but it is usually within an hour.
- After that, your storage account type in the new main region is automatically switched to locally redundant storage (LRS) after the failover. For the account, you can re-enable geo-redundant storage (GRS) or read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS). It’s worth noting that changing from LRS to GRS or RA-GRS incurs a fee. The expense is due to network egress charges associated with re-replicating data to a new secondary region.
- Further, Microsoft begins replicating the data in your account to the new secondary region when you re-enable GRS for your storage account. Many factors influence replication time, including:
- The total number of things in the storage account, as well as their size. It can take longer to process a big number of little things than it does to process a smaller number of larger objects.
- The CPU, RAM, disc, and WAN capabilities that are available for background replication. Geo replication takes a back seat to live traffic.
- Next, the amount of snapshots per blob if utilising Blob storage.
- The data partitioning technique if you’re utilising Table storage. You can’t scale the replication process beyond the amount of partition keys you’re using.
Reference documentation – Initiate a storage account failover

