- Expands to Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- It is a network protocol to automatically assign an IP address and other network configuration to a computer from a defined range of numbers (i.e., a scope) configured for a given network.
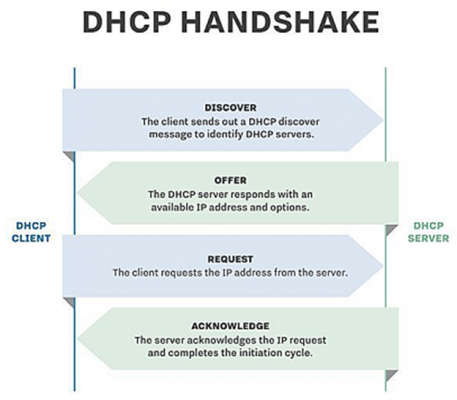
- Steps in Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol assignment of an IP address when a system begin as:
- A user turns on a computer with a DHCP client.
- The client computer sends a broadcast request (called a DISCOVER or DHCPDISCOVER), looking for a DHCP server to answer.
- The router directs the DISCOVER packet to the correct Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server.
- The server receives the DISCOVER packet.
- As per availability and policies configuration, appropriate address is found by server to be given to client
- server temporarily reserves address and other details for client
- details get transfer to DHCPOFFER packet
- Other services have same configuration process like DNS servers, WINS servers, NTP servers
- The client sends a REQUEST (or DHCPREQUEST) packet, letting the server know that it intends to use the address.
- The server sends an ACK (or DHCPACK) packet, confirming that the client has a been given a lease on the address for a server-specified period of time.
- DHCP server uses IP-addresses allocates, as
- Dynamic allocation- IP addresses gets assign for a controllable time period, from a range
- Automatic allocation- Permanent assignment of IP address, from a range
- Static allocation- IP address based on a table with MAC address.
- DHCP uses
- UDP port 67 for sending data to server
- UDP port 68 for data to the client.
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol communications are connectionless.
- DHCP clients and servers on the same subnet communicate via UDP broadcasts else
For different subnets, there is the use of DHCP Helper or DHCP Relay Agent.
AWS Certified Advanced Networking Specialty Free Practice TestTake a Quiz
