Piping Inspector (API 570)

API’s Individual Certification Programs (ICP) is a certification and evaluation body. It has been trying to provide adequately evaluated, competent, and experienced technical and inspection employees to the petroleum and petrochemical sectors since 1989. The certification processes are based on industry-developed standards that are well-known. As a result, this API 570 Piping Inspector certification will enable you to develop a career path, increase your abilities via learning, and strengthen your overall job performance, allowing you to contribute significantly to the safety and quality of industry operations.
Prerequisite for the API 570 exam:
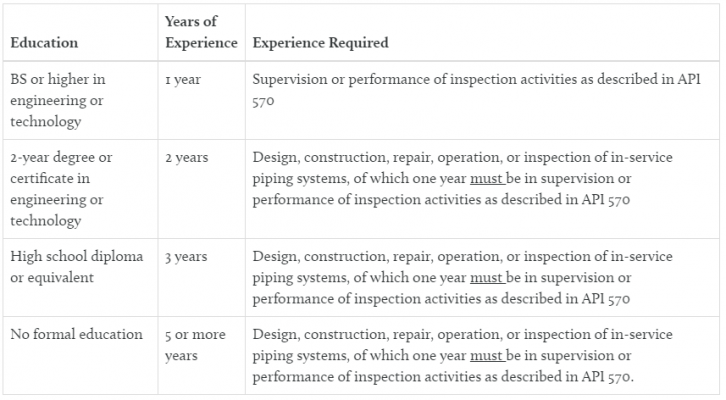
You must have a combination of education and expertise with in-service metallic piping systems to be considered for this position. The experience must have been gained during the last ten years while working for or under contract with an authorised inspection agency as specified by API 570. You can also use the chart below to determine your eligibility:
Exam Details API 570
| Exam Name: Piping Inspector | |
| Code API 570 | |
| Time Duration: 7.5 hours | |
| Exam Language: English | |
| Exam Format: Multiple Choice | |
| Number of Questions: 150 Questions | |
| Exam Fee: API member fee: $730, Non-Member fee: $940 | |
| Pass Score 70% and above |
Exam Scheduling API 570
Follow the following steps to schedule your Piping Inspector Exam:
- Go to Prometric’s website at www.prometric.com/apiexams
- Locate a testing center.
- Schedule your computer-based test (CBT) location, date and time
- Confirm your exam appointment details.

For further exam related details visit: Piping Inspector (API 570) FAQ
Course Structure
Following is the brief outline of the Piping Inspector (API 570) certification course structure:

I. API Authorized Piping Inspectors should be able to inspect and calculate in-service deterioration, repairs, rerates, and changes, such as those listed in the eight categories below:
1. CORROSION RATES AND INSPECTION INTERVALS
The Inspector should be able to understand inspection data and determine the thickness measurement and visual external inspection intervals. The Inspector must be able to calculate:
- Corrosion Rates
- Remaining Service Life
- Inspection Interval
2.WELD JOINT QUALITY FACTORS AND CASTING QUALITY FACTORS
The inspector should be able to determine the weld joint quality factor “Ej” of a longitudinal pipe weld joint. The inspector should be able to determine:
- Casting Quality factor
- Weld Joint Quality factors
- Increased Joint Quality Factors by performing supplemental NDE
Since the joint factor, Ej is utilized in the calculations for determining required thickness or internal design pressure, determining the weld joint quality factor could be part of an internal pressure problem.
3.INTERNAL PRESSURE / MINIMUM THICKNESS OF PIPE
The inspector should be able to determine:
- The minimum required thickness or pressure design thickness of a straight pipe section for internal pressure only
- The minimum required thickness of a permanent blank for a given design pressure
- The “MAWP” of corroded pipe, compensating for expected corrosion loss at the next inspection
The inspector should also be able to compensate for the corrosion allowance.
4.PRESSURE TESTING
The inspector should be able to:
- Demonstrate knowledge concerning hydrostatic leak testing
- Demonstrate knowledge concerning pneumatic leak testing
- Calculate a hydrostatic or pneumatic leak test pressure
5.IMPACT TESTING
The inspector should be able to:
- Determine the minimum metal temperature of a material, which is exempt from impact testing
- Determine the minimum required Charpy V-notch impact values of a given material.
6.PREHEATING AND HEAT TREATMENT REQUIREMENTS
Which weld sizes require preheating and/or heat treatment should be determined by the inspector. The inspector should also be able to calculate the preheat temperature that is required or suggested.
7.THERMAL EXPANSION
The inspector should be able to determine the total thermal expansion of material between temperatures.
8.MINIMUM WALL THICKNESS & WORKING PRESSURES FOR FLANGES
The inspector should be able to determine the minimum wall thickness and working pressure requirements for flanges.
The inspector should also be able to:
- Determine the working pressure and minimum/maximum system hydrostatic test pressure for a flange of specified material and temperature
- Determine the minimum dimensions of a given flange
- Determining the maximum working pressure of a flange when given the design temperature, flange material, and flange class.
- Determine the maximum temperature of a flange when given the design pressure, flange material, and flange class.
- Determine the most cost-effective flange when given the design pressure, design temperature, and flange material.
II. WELDING PROCEDURE AND QUALIFICATION EVALUATION
1.ASME BOILER AND PRESSURE VESSEL CODE
The inspector should be able to examine a Procedure Qualification Record, Welding Procedure Specification, and Welder Performance Qualification to determine the following:
- Determine whether the procedure and qualification records comply with the applicable ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, as well as any additional API-570 criteria. The following items will be discussed during the weld procedure review:Weld Procedure Specification (WPS)
- Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)
- Welder Performance Qualification (WPQ)
- Check to see if all of the necessary important and non-essential factors have been addressed. (The WPS/PQR will not include any additional necessary variables.)
- Determine whether the mechanical tests stated on PQR are the correct number and type of tests, and whether the results are acceptable.
- Determine whether the welder meets the WPS requirements for a production weld.
WELD PROCEDURE REVIEW MAY INCLUDE SMAW, GTAW, GMAW, OR SAW, WITH THE FOLLOWING LIMITATIONS:
- No more than one process will be included on a single WPS, PQR or WPQ and the WPS to be reviewed will be
supported by a single PQR. - Filler metals will be limited to one-per-process for SMAW, GTAW, GMAW, or SAW
- The PQR will be the supporting PQR for the WPS.
- The WPQ test coupon is to be welded in accordance with a qualified WPS.
- Base metals will be limited to P1, P3, P4, P5, and P8.
- Dissimilar base metal joints, and dissimilar thicknesses of base metals will be excluded.
- Special weld processes such as corrosion-resistant weld metal overlay, hard-facing overlay, and dissimilar metal
welds with buttering of ferritic member will be excluded. - For P1, P3, P4, and P5, for the purpose of the examination the lower transition temperature will be 1330°F and the upper transformation temperature will be 1600°F
2. ASME B31.3
The inspector should be familiar with and understand the general rules for welding in ASME B31.3, Chapter V such as:
- Typical joints and definitions
- Weld sizes
- Restrictions on joints
- Maximum allowable reinforcement
- Inspection requirements
- Preheating and Heat Treatment
3. API Standard 570
The inspector should be familiar with and understand any rules for welding in API-570. Any rules for welding given in API570 shall take precedence over those covering the same areas in ASME, B31.3.
4. The inspector shall be familiar with all the requirements of and information in API RP 577
III. NONDESTRUCTIVE EXAMINATION
1. ASME Section V, Nondestructive Examination
- Article 1, General Requirements
- Article 2, Radiographic Examination
- Next, Article 6, Liquid Penetrant Examination (Including mandatory appendices II and III)
- Article 7, Magnetic Particle Examination (Yoke and Prod techniques only)
- After that, Article 9, Visual Examination
- Article 10, Leak Testing (Including Mandatory Appendix I Bubble Test –Direct Pressure Technique
- Article 23, Ultrasonic Standards, Section SE–797 only – Standard practice for measuring thickness by manual ultrasonic pulse-echo contact method
2. ASME B31.3 and API-570: General nondestructive examination requirements:
- ASME B31.3: The inspector should be familiar with and understand the general rules for NDE (Chapter VI).
- API Standard 570: The inspector should be familiar with and understand the general rules for NDE in API-570.
IV: PRACTICAL KNOWLEDGE – GENERAL
- Organization and Certification Requirements.
- Types and Definitions of Maintenance Inspections.
- Welding on Piping
- Corrosion and Minimum Thickness Evaluation.
- Estimated Remaining Life.
- Inspection Interval Determination and Issues Affecting Intervals.
- Maintenance Inspection Safety Practices.
- Inspection Records and Reports.
- Repairs/Alterations/Reratings to Piping.
- Rerating Piping.
- Pressure Testing After Repairs, Alterations, or Rerating
- Pressure Temperature Ratings
- Markings
- Materials
- Dimensions
- Test
- Limiting Dimensions of Gaskets
- Methods for Establishing Pressure-Temperature Ratings
- Methods of performing positive material identification and related record keeping
Preparation Guide
Refer the following preparation guide to get a brief understanding about the whole process flow of this examination and how you should proceed.

Learning resources
It is recommended to go through the following resources to excel in the examination:
1. Publications Effectivity Sheet
Questions on the API 570 exam are derived from the set of publications recommended by API. Only the specific sections of publications that are listed on the Effectivity Sheet will be available to you during the open-book portion of the exam. So, do proper research before you buy books. API has released the API 570 Publications Effectivity Sheet which consists of various publications, topics to focus upon.
2. API Body Of Knowledge
API Body Of Knowledge specifies the different sets of books to be referred for appearing in the Piping Inspector examination. The API Piping Inspector examination consists of two parts. The closed-book part tests the candidate on knowledge and tasks requiring an everyday working knowledge of API Standard 570 and the applicable reference documents. The open-book portion of the examination requires the use of more detailed information that the inspector is expected to be able to find in the documents, but would not normally be committed to memory. During the exam, applicants will be expected to choose the best answer from the options provided.
REFERENCE PUBLICATIONS:
A. API Publications:
- API Standard 570, Inspection, Repair, Alteration, and Rerating of In-Service Piping Systems
- Next, API Recommended Practice 571, Damage mechanisms Affecting Fixed Equipment in the Refining Industry
- Then, API Recommended Practice 574, Inspection Practices for Piping System Components
- API Recommended Practice 577, Welding Inspection and Metallurgy
- API Recommended Practice 578, Guidelines for a Material Verification Program (MVP) for New and Existing Assets
B. ASME Publications:
- American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code:
- Section V, Nondestructive Examination
- Section IX, Qualification Standard for Welding, Brazing, and Fusion Procedures; Welders; Brazers; and
- Welding, Brazing and Fusing Operators
- B16.5, Pipe Flanges, and Flanged Fittings, B31.3, Process Piping
Practice Tests
The Piping Inspector is an exam that focuses on both your theoretical and practical knowledge. For practical you have to have on-site work experience in addition to what you have learned over the whole training process of API Piping Inspector course. When you are done all your preparation it is always advisable to go for some mock test before you plan to sit for the actual examination. This will not only boost your confidence but will also make you aware of the weak portions in your preparation and which require some more focus and hard work.
Further, taking real-time practice tests will also release you from exam fear and exam pressure. You can go for testpreptraining practice test which is prepared by experts and is based on the API exam pattern, thus giving you a feel of actual exam. So, take the practice test and Start Practicing Now!

