Design Factors
Design factors are factors that which influences the design of an organizational governance system. The factors also position the organizational governance system in successfully using the I&T infrastructure.
Categorization
Design factors include the goals cascade of an enterprise and includes additional design factors broadly categorized as:
- Contextual—Design factors that are outside the control of the enterprise (e.g., its size, geopolitical situation or threat landscape)
- Strategic—Design factors that reflect decisions made by the enterprise (e.g., the enterprise strategy, the role of IT for the success of the enterprise or formulation of risk appetite)
- Tactical—Design factors that are based on implementation choices regarding resourcing models (e.g., outsourcing, cloud), IT methods (e.g., Agile, DevOps) and technology adoption choices (e.g., bleeding/leading edge.).
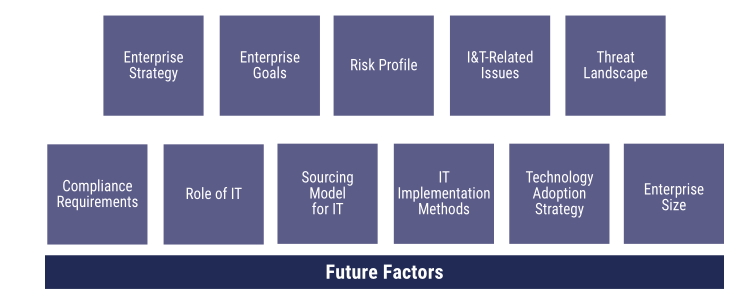
There are 11 design factors in the COBIT 2019 Design Guide, which further can refine as per the requirement.
Design Factors
Design factors include any combination of the following
- Enterprise strategy—Enterprises can have different strategies, expressed as specific archetypes. Organizations usually have a primary strategy and, at most, one secondary strategy.
- Enterprise goals– They supports the enterprise strategy as the enterprise strategy is realized by the achievement of enterprise goals which are defined in the COBIT framework.
- Risk profile- The present risk company is exposed to and which risk areas needs to be addressed.
- I&T-related issues—A related method for an I&T risk assessment for the enterprise to identify the I&T-related issues it currently faces
- Threat landscape – It can be normal or high.
- Compliance requirements – It can be normal or high or low.
- Role of IT – It can be factory, support, turnaround or strategic.
- Sourcing model for IT – It can be Outsourcing, cloud, Insourced or hybrid.
- IT implementation methods – It can be agile, DevOps, Traditional or hybrid
- Technology adoption strategy – It can be First mover, follower or Slow adopter
Are you preparing to take the COBIT 2019 Foundation exam?Take a Quiz

