CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501)

CompTIA Security+ certification validates the necessary baseline skills to perform core security functions and pursue an IT security career. Moreover, CompTIA Security+ is the first security certification IT professionals should earn. This certification exam establishes the core knowledge required for cybersecurity roles and provides a springboard to intermediate-level cybersecurity jobs. This also provides best practices in hands-on trouble-shooting to ensure security professionals have practical security problem-solving skills. However, Security+ is compliant with ISO 17024 standards and approved by the US DoD to meet directive 8140/8570.01-M requirements.
CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) English language exam is retiring on July 31, 2021. A new exam Security+ (SY0-601) is now available.
Knowledge Required for the Exam
The CompTIA Security+ certification is good for IT security professional who has:
- At least two years of experience in IT administration with knowledge in security
- Day-to-day technical information security experience
- Broad knowledge of security concerns and implementation
Target Areas
The CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) certification exam is apt for professionals involved in:
- Information security
- Network security
- System administration
- Security analysis
- Penetration testing
- IT auditing
Why is the CompTIA Security+ exam different?
This certification exam assesses baseline cybersecurity skills and has performance-based questions on the exam. Moreover, Security+ emphasizes hands-on practical skills, ensuring the security professional is better prepared to problem solve a wider variety of issues. This focuses on the latest trends and techniques in risk management, risk mitigation, threat management, and intrusion detection.
Skills Enhancement
Candidates for this certification exam will be able to:
 Identify various types of compromise with an understanding of penetration testing and vulnerability scanning concepts.
Identify various types of compromise with an understanding of penetration testing and vulnerability scanning concepts.
 Perform operations like Installing, configuring, and deploying network components while assessing and troubleshooting issues to support organizational security.
Perform operations like Installing, configuring, and deploying network components while assessing and troubleshooting issues to support organizational security.
 Implementing secure network architecture concepts and systems design.
Implementing secure network architecture concepts and systems design.
 Installing and configuring identity and access services, as well as management controls.
Installing and configuring identity and access services, as well as management controls.
 Summarize risk management best practices and business impact.
Summarize risk management best practices and business impact.
 Configure and install wireless security settings and implement the public key infrastructure.
Configure and install wireless security settings and implement the public key infrastructure.
Exam Format
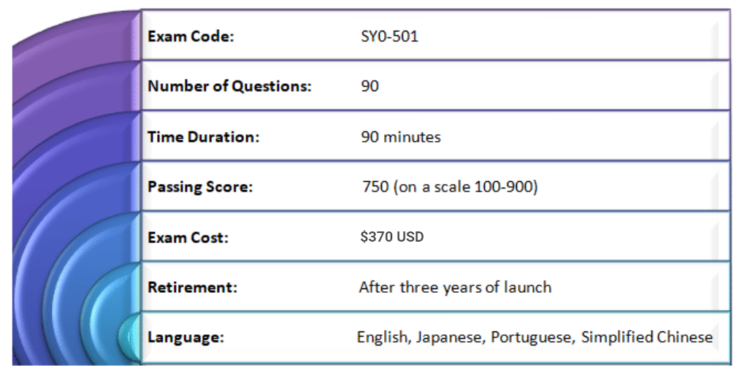
CompTIA provides all the accessible information to the candidates for the SY0-501 exam. The CompTIA Security+ exam will have a maximum of 90 questions. In which the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) exam questions will include types like multiple choice and performance-based questions with a time duration of 90 minutes. To pass the exam, candidates have to score a minimum of 750 (on a scale of 100-900). However, the exam is available in English, Japanese, Portuguese and Simplified Chinese. SY0-501 exam will cost $370 USD and this exam retires usually after three years of launch.
Applying for the Exam
CompTIA provides two ways to take the SY0-501 exam that are either online or in-person. In which online testing provides convenience to test for your certification from any quiet, distraction-free, and secure location at any time. And, it also provides flexibility to schedule your exam at any hour convenient with technical support if something goes wrong during the exam. On the other hand, In-person testing provides testing options at any of the thousands of Pearson VUE test centers located around the world. The exam can be scheduled at, 
Course Structure
The CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) exam objectives include:
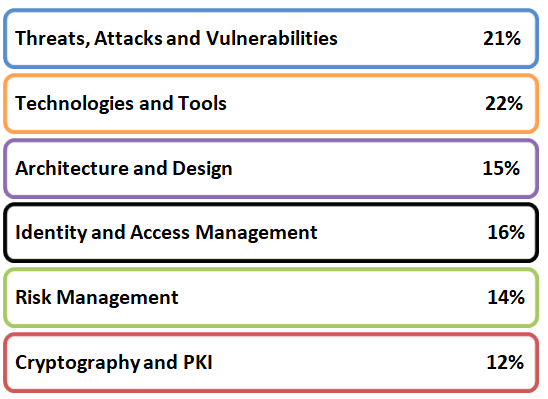
Topic 1: Threats, Attacks and Vulnerabilities
1.1 Given a scenario for analyzing indicators of compromise and determining the type of malware.
- Viruses
- Crypto-malware
- Ransomware
- Worm
- Trojan
- Rootkit
- Keylogger
- Adware
1.2 Comparing and contrasting types of attacks.
- Social engineering
- Application/service attacks
- Wireless attacks
- Cryptographic attacks
1.3 Explaining the threat actor types and attributes.
- Types of actors
- Attributes of actors
- Use of open-source intelligence
1.4 Describing penetration testing concepts.
- Active reconnaissance
- Passive reconnaissance
- Pivot
- Initial exploitation
- Persistence
- Escalation of privilege
- Black box
- White box
- Gray box
1.5 Explaining vulnerability scanning concepts.
- Passively test security controls
- Identify vulnerability
- Identifying lack of security controls and common misconfigurations
- Intrusive vs. non-intrusive
- Credentialed vs. non-credentialed
- False positive
1.6 Defining the impact associated with types of vulnerabilities.
- Race conditions
- Improper input handling and error handling
- Misconfiguration/weak configuration
- Default configuration
- Resource exhaustion
- Untrained users
- Improperly configured accounts
- Vulnerable business processes
- Weak cipher suites and implementations
- Memory/buffer vulnerability
- System sprawl/undocumented assets
- Architecture/design weaknesses
- New threats/zero day
- Improper certificate and key management
Topic 2: Technologies and Tools
2.1 Installing and configuring network components with both hardware and software-based to support organizational security.
- Firewall
- VPN concentrator
- NIPS/NIDS
- Router
- Switch
- Proxy
- Load balancer
- Access point
- SIEM
- DLP
- NAC
- Mail gateway
- Bridge
- SSL/TLS accelerators
- SSL decryptors
- Media gateway
- Hardware security module
2.2 A scenario for using appropriate software tools to assess the security posture of an organization.
- Protocol analyzer
- Network scanners
- Wireless scanners/cracker
- Password cracker
- Vulnerability scanner
- Configuration compliance scanner
- Exploitation frameworks
- Data sanitization tools
- Steganography tools
- Honeypot
- Backup utilities
- Banner grabbing
- Passive vs. active
- Command line tools
2.3 Given a scenario for troubleshooting common security issues.
- Unencrypted credentials/clear text
- Logs and events anomalies
- Permission issues
- Access violations
- Certificate issues
- Data exfiltration
- Misconfigured devices
- Weak security configurations
- Personnel issues
- Unauthorized software
- Baseline deviation
- License compliance violation
- Asset management
- Authentication issues
2.4 With a scenario to analyze and interpret the output from security technologies
- HIDS/HIPS
- Antivirus
- File integrity check
- Host-based firewall
- Application whitelisting
- Removable media control
- Advanced malware tools
- Patch management tools
- UTM
- DLP
- Data execution prevention
- Web application firewall
2.5 Scenario for deploying mobile devices securely.
- Connection methods
- Mobile device management concepts
- Enforcement and monitoring for:
- Deployment models
2.6 Given a scenario for implementing secure protocols.
- Protocols
- Use cases
Topic 3: Architecture and Design
3.1 Explaining use cases and purpose for frameworks including best practices and secure configuration guides.
- Industry-standard frameworks and reference architectures
- Benchmarks/secure configuration guides
- Defense-in-depth/layered security
3.2 Given a scenario for implementing secure network architecture concepts.
- Zones/topologies
- Segregation/segmentation/isolation
- Tunneling/VPN
- Security device/technology placement
- SDN
3.3 A scenario to implement secure systems design.
- Hardware/firmware security
- Operating systems
- Peripherals
3.4 Explaining the importance of secure staging deployment concepts.
- Sandboxing
- Environment
- Secure baseline
- Integrity measurement
3.5 Describing the security implications of embedded systems.
- SCADA/ICS
- Smart devices/IoT
- HVAC
- SoC
- RTOS
- Printers/MFDs
- Camera systems
- Special purpose
3.6 Summarizing secure application development and deployment concepts.
- Development life-cycle models
- Secure DevOps
- Version control and change management
- Provisioning and deprovisioning
- Secure coding techniques
- Code quality and testing
- Compiled vs. runtime code
3.7 Outlining cloud and virtualization concepts.
- Hypervisor
- VM sprawl avoidance
- VM escape protection
- Cloud storage
- Deployment models for cloud
- On-premise vs. hosted vs. cloud
- VDI/VDE
- Cloud access security broker
- Security as a Service
3.8 Explaining use of resiliency and automation strategies reduce risk.
- Automation/scripting
- Templates
- Master image
- Non-persistence
- Elasticity
- Scalability
- Distributive allocation
- Redundancy
- Fault tolerance
- High availability
- RAID
3.9 Describing the importance of physical security controls.
- Lighting
- Signs
- Fencing/gate/cage
- Security guards
- Alarms
- Safe
- Secure cabinets/enclosures
- Protected distribution/Protected cabling
- Air Gap
- Mantrap
- Faraday cage
- Lock types
- Biometrics
- Barricades/bollards
- Tokens/cards
- Environmental controls
- Cable locks
- Screen filters
- Cameras
- Motion detection
- Logs
- Infrared detection
- Key management
Topic 4: Identity and Access Management
4.1 Contrasting and comparing identity and access management concepts
- Identification, authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA)
- Multi Factor authentication
- Federation
- Single sign-on
- Transitive trust
4.2 Given a scenario for installing and configuring identity and access services.
- LDAP
- Kerberos
- TACACS+
- CHAP
- PAP
- MSCHAP
- RADIUS
- SAML
- OpenID Connect
- OAUTH
- Shibboleth
- Secure token
- NTLM
4.3 A scenario to implement identity and access management controls.
- Access control models
- Physical access control
- Biometric factors
- Tokens
- Certificate-based authentication
- File system security
- Database security
4.4 Scenario for differentiating common account management practices.
- Account types
- General Concepts
- Account policy enforcement
Topic 5: Risk Management
5.1 Explaining the importance of policies, plans and procedures related to organizational security.
- Standard operating procedure
- Agreement types
- Personnel management
- General security policies
5.2 Summarizing business impact analysis concepts.
- RTO/RPO
- MTBF
- MTTR
- Mission-essential functions
- Identification of critical systems
- Single point of failure
- Impact
- Privacy impact assessment
- Privacy threshold assessment
5.3 Explaining risk management processes and concepts.
- Threat assessment
- Risk assessment
- Change management
5.4 Given a scenario to follow incident response procedures
- Incident response plan
- Incident response process
5.5 Outlining the basic concepts of forensics.
- Order of volatility
- Chain of custody
- Legal hold
- Data acquisition
- Preservation
- Recovery
- Strategic intelligence/counterintelligence gathering
- Track man-hours
5.6 Explaining disaster recovery and continuity of operation concepts.
- Recovery sites
- Order of restoration
- Backup concepts
- Geographic considerations
- Continuity of operation planning
5.7 Comparing and contrasting various types of controls.
- Deterrent
- Preventive
- Detective
- Corrective
- Compensating
- Technical
- Administrative
5.8 A scenario to carry out data security and privacy practices.
- Data destruction and media sanitization
- Sensitivity labeling and handling of Data
- Data roles
- Retention of Data
- Legal and compliance
Topic 6: Cryptography and PKI
6.1 Comparing and contrasting basic concepts of cryptography
- Symmetric algorithms
- Modes of operation
- Asymmetric algorithms
- Hashing
- Salt, IV, nonce
- Elliptic curve
- Weak/deprecated algorithms
- Key exchange
- Digital signatures
- Diffusion
- Confusion
- Collision
- Steganography
- Obfuscation
- Stream vs. block
- Key strength
- Session keys
- Ephemeral key
- Secret algorithm
- Data in transit, rest and use
- Random/pseudo-random number generation
- Key stretching
- Implementation vs. algorithm selection
- Perfect forward secrecy
- Security through obscurity
- Common use cases
6.2 Describing cryptography algorithms and their basic characteristics.
- Symmetric algorithms
- Cipher modes
- Asymmetric algorithms
- Hashing algorithms
- Key stretching algorithms
- Obfuscation
6.3 Given a scenario for installing and configuring wireless security settings
- Cryptographic protocols
- Authentication protocols
- Methods
6.4 A scenario to implement public key infrastructure.
- Components
- Concepts
- Types of certificates
- Certificate formats
Testing Policies
CompTIA provides various exam testing policies for candidates that need to be taken care of. Moreover, these policies will help candidates to understand the certification exam procedure. Some of the policies are:
Exam Rescheduling:
Candidates who want to reschedule the exam must contact Pearson VUE at least a minimum of 24 hours prior to your exam appointment. That is to say, rescheduling an exam less than 24 hours prior to your appointment or failure to appear for your appointment will result in the forfeiture of your exam fee.
Exam Language:
CompTIA exam can be given in English language. However, for those who are in non-English speaking countries, a 30-minute time extension will be given during exams delivery. As all of CompTIA’s exams are available in English, ESL is not available in English-speaking countries. During registration for the exams at Pearson VUE, ESL will be granted to candidates if the country is eligible.
EXAM SCORING
CompTIA monitors the performance of all exams to ensure the validity of exam results. However, during monitoring of exams, CompTIA may classify scores as indeterminate when there are discrepancies for which there is no reasonable explanation. Scores that are unclear will not be considered valid and will not be eligible for certification. And, the exam passing scores are set using statistical analysis and are subject to change. After the exam completion, candidates will receive a score report that contains important information regarding the outcome of the exam. Moreover, CompTIA does not publish exam passing rates because exam questions and passing rates are subject to change without notice. Further, to understand more about the CompTIA agreements and policies, you can take a look at the CompTIA exam test policies.
For more Queries Visit: CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) Exam FAQs
Preparing for CompTIA SY0-501 Exam
For the CompTIA Security+ exam, there are various methods provided below to prepare and pass the exam with good scores. Moreover, using this will help you in creating CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) study notes as well.

eLearning with CertMaster for Security+
CompTIA gives candidates to have access to the eLearning solution that is CertMaster Learn. CertMaster Learn is interactive and self-paced that includes a customizable learning plan and performance-based questions for Security+. However, this will help in taking you on a path of consistent learning toward your certification exam.
CompTIA Labs for Security+
CompTIA Labs for Security+ helps the candidate to acquire the necessary hands-on skills for Security+ certification. Moreover, they will develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter and the practical aspects of the Security certification exam objectives. CompTIA Labs also helps candidates to address the practical aspects of Security exam objectives and complement prior training through access to real equipment and software environments.
Exam Preparation with CertMaster Practice: Security+
CertMaster Practice is a tool that assesses your knowledge and exam readiness. This is filled with CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) study material, question-first design, real-time learning analytics, and content refreshers. Moreover, This will help candidates to prepare well by confirming strong areas and filling knowledge gaps in weak areas during studying.
Study Guides for Security+
While studying for the exam, it is good to prefer traditional textbook style learning, which is packed with informative and accessible content covering all Security exam objectives. However, for the SY0-501 exam, CompTIA provides a study guide that is, CompTIA Security+ SY0-501 Certification Study Guide.
 This CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) study guide will teach candidates the fundamental principles of installing and configuring cybersecurity controls and participating in incident response and risk mitigation.
This CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) study guide will teach candidates the fundamental principles of installing and configuring cybersecurity controls and participating in incident response and risk mitigation.
Instructor-Led Training
For those looking for in-classroom or live online training, CompTIA provides best-in-class instructor-led training for both individuals and teams. These CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) training sessions will help the candidates to understand the concepts more accurately in a short duration.
Practice Tests
Practice tests are important during exam preparation time. That is to say, by assessing yourself with the CompTIA Security+ (SY0-501) practice tests you will know about your weak and strong areas. We all know time plays an essential role during the exam. So, by practicing you will be able to improve your answering skills that will result in saving a lot of time. Moreover, the best way to start doing practice tests is after completing one full topic as this will work as a revision part for you.
Joining Study Groups
During the exam preparation time, it is good to join study groups. These groups will help you to stay connected with the other people who are on the same pathway as yours. Moreover, here you can start any discussion about the issue related to the exam or any query. By doing so, you will get the best possible answer to your query.
Start Prepare for CompTIA SY0-501 Exam Now!


