- VPC is networking layer for Amazon EC2,
- You can build a private virtual network in AWS.
- control the various aspects of the Amazon VPC,
including –
- Selecting own IP address range
- Creating own subnets
- Configuring own route tables, network gateways, and security settings.
- In a region, create multiple Amazon VPCs
- each VPC is logically isolated even if sharing IP address space
- Specify IPv4 address range during VPC creation
- Address range of VPC cannot be changed after VPC is created.
- VPC address range may be large as /16 (65,536 available addresses) or as small as /28 (16 available addresses)
- VPC address range should not overlap any other network with which they are to be connected.
VPC Components
- Subnets
- segment of an VPC’s IP address range to launch EC2 instances, Amazon RDS databases, and other AWS resources.
- smallest subnet is a /28 (or 16 IP addresses).
- AWS reserves first four IP addresses and the last IP address of every subnet for internal networking purposes.
- Route tables
- A logical construct within VPC having set of rules (or routes) applied to subnet and used to determine where network traffic is directed.
- With route table EC2 instances in different subnets in a VPC to communicate with each other.
- Route table has default route called local route, to communication within Amazon VPC, and this route cannot be modified or removed.
- DHCP or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is
used to configure –
- DHCP passes configuration information to hosts on a TCP/IP network like domain name, domain name server, and the netbios-node-type.
- AWS
automatically creates and associates a DHCP option set for the Amazon VPC upon
creation and sets two options:
- domain-name-servers (defaulted to AmazonProvidedDNS)
- domain-name (defaulted to the domain name for region).
- AmazonProvidedDNS is an Amazon Domain Name System (DNS) server, and this option enables DNS for instances that need to communicate over the Amazon VPC’s IGW.
- Security groups
- A virtual stateful firewall controlling inbound and outbound network traffic to AWS resources and EC2 instances.
- EC2 instances should be launched into a security group.
- If not specified at launch, then instance will be in default security group for VPC, which allows communication between all resources within security group, allows all outbound traffic, and denies all other traffic.
- Network Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- Acts as stateless firewall on a subnet level.
- It is list of rules, which is sequenced by numbers
- AWS evaluates the numbered list, starting with lowest values, first
- Each rule tells about, which traffic to allow or deny in/out of specific subnet
- Amazon VPCs have modifiable default network ACL associated with every subnet that allows all inbound and outbound traffic.
Optional Components of Amazon VPC
Internet Gateways (IGWs)
- A horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available Amazon VPC component for communication between instances in VPC and Internet.
- It gives a target in VPC route tables for Internet-routable traffic
- performs network address translation for instances having public IP addresses.
- All the EC2 instances, present in a VPC, know only their own private IP addresses
- IGW has a map of EIP address (public IP address of the instance) and the private IP address
- IGW is responsible to translate requests to and fro, amongst instance and internet
Elastic IP (EIP) addresses
- AWS manages a pool of public IP addresses in each region
- The public IP addresses in AWS region, can be assigned to resources in the VPC
- It is a static, public IP address in pool for region
- can allocate it to account (pull from the pool)
- Can release them (return to the pool).
- It is a set of IP addresses that remain fixed while the underlying infrastructure may change over time.
Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs)
- A virtual network interface that can attach to an instance in an Amazon VPC.
- ENIs are only available within an VPC
- They are associated with a subnet upon creation.
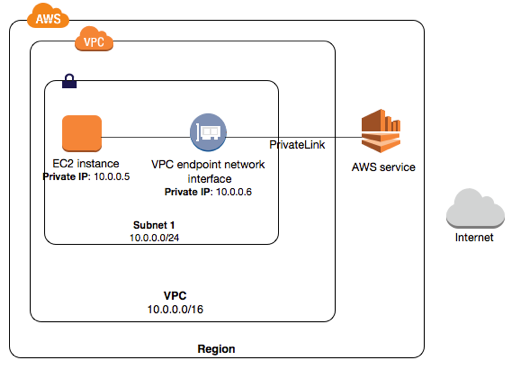
Endpoints
- It allows to create a private connection between VPC and another AWS service without access over Internet or NAT instance, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect.
- multiple endpoints can be made, for a single service
Peering
- It refers to a networking connection but, between 2 VPCs hence called as VPC peering connection
- It enables instances in either Amazon VPC to communicate with each other as if they are within the same network.
- It is neither a gateway nor an VPN connection
- Peering helps to prevent SPOF or single point of failure, for communication.
- Connections are developed by using a
request/accept protocol amongst the VPCs, as
- First, the requesting VPC owner will send request to peer to peer VPC’s owner.
- Identification
of requested peer is done by
- Only VPC ID if both are in same AWS account
- Both account ID and VPC ID are used if both are in different accounts
- Peer VPC’s owner need to accept within one week of request receipt, else it expires
AWS Certified Security - Specialty Free Practice TestTake a Quiz
