OpsWorks Stacks & Layers
- It provides a simple and flexible way to create and manage stacks and applications.
- Deploy and monitor applications in your stacks.
- It does not require or create Chef servers;
- Performs some of the work of a Chef server for you.
- Monitors instance health, and provisions new instances for you, when necessary, by using Auto Healing and Auto Scaling.
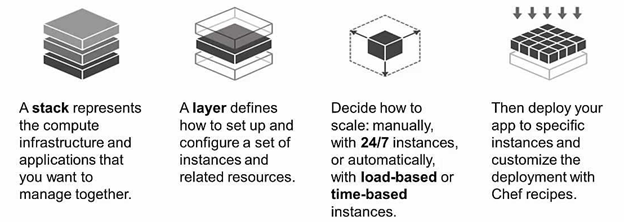
OpsWorks Stacks
- stack represents set of instances to manage collectively
- Serves as a container
- stack have common purpose like serving applications.
- stack handles tasks applying to group of instances as a whole
- An example of stack serving web applications has
- A set of application server instances for incoming traffic
- A load balancer instance
- A database instance
- Best practice to have multiple stacks that represent different environments.
- Usually a set of stacks includes
- A development stack to add features and fix bugs for developers
- A staging stack to verify updates before making it production
- A production stack
Creating a Stack
To create a new stack
- Go to the AWS OpsWorks Stacks dashboard
- click Add stack.
The Add Stack page options
- Stack name – (Required) identify the stack. Unique not required. stack ID a GUID, identifies the stack and can be used in commands.
- Region – (Required) region where instances will be launched.
- VPC – (Optional) The VPC ID, where stack is to be launched. Also supports EC2 Classic, with No VPC. VPC needed if not supporting EC2 Classic.
- Default Availability Zone/Default subnet – (Optional) It depends, if creating stack in a VPC:
- If supporting EC2 Classic can set VPC to No VPC.
- If no EC2 Classic or want a VPC, this field is labeled Default subnet.
- Default operating system – (Optional) Any one from built-in Linux operating systems, Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 or a custom AMI based on one of the supported operating systems.
- Default SSH key – (Optional) Amazon EC2 key pair from the stack’s region. The default value is none.
- Chef version – Chef version being selected
- Use custom Chef cookbooks – Enable installing custom Chef cookbooks on the stack’s instances.
- For Chef 12, the default setting is Yes. For Chef 11, The default setting is No.
- Stack color – (Optional) The hue used to represent the stack on the AWS OpsWorks Stacks console.
- Stack tags – Apply tags at the stack and layer level and all resource within gets tagged.
- Default root device type – Determines the type of storage to be used for the instance’s root volume.
- IAM role – (Optional) The stack’s AWS IAM role, to interact with AWS
- Default IAM instance profile – (Optional) The default IAM role to be associated with the stack’s Amazon EC2 instances.
- Hostname theme – (Optional) string to generate a default hostname for each instance.
- Custom JSON – (Optional) One or more custom attributes, formatted as a JSON structure.
- You cannot modify the region or VPC ID.
Running a stack in a VPC involves following steps
- Create an appropriately configured VPC, by using the Amazon VPC console or API, or an AWS CloudFormation template.
- Specify the VPC ID when you create the stack.
- Launch the stack’s instances in the appropriate subnet.
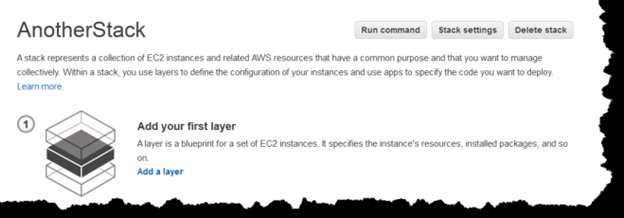
OpsWorks Layers
- Every stack contains at least one layers or more
- Every layer refers to a stack component like load balancer or a set of servers.
- Every layer should have a minimum of one instance or more.
- Every instance must be a member of a minimum one layer, except for registered instances.
- Instances may be a member of multiple layers.
- With multiple layers in an instance
- Reduce expenses by hosting the multiple server like database and load balancer, on same instance.
- For administration, add another admin server instances to that layer.
- To add the first OpsWorks layer
- Click Add Layer.
- On the Add Layer page, select the appropriate layer, showing the layer’s configuration options.
- Configure the layer and click Add Layer to add it to stack.
- To edit an OpsWorks layer
- In navigation pane, click Layers.
- On the Layers page, select a layer name and open its details page
- Click Edit and then select the appropriate tab: General Settings, Recipes, Network, EBS Volumes, or Security.
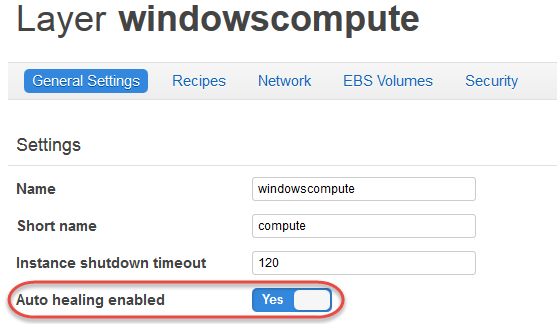
- OpsWorks Layer’s Configuration Main Settings
- Auto healing enabled – If auto healing is enabled for the layer’s instances. The default setting is Yes.
- Custom JSON – Data in JSON format that is passed to your Chef recipes for all instances in this layer. You can use this, for example, to pass data to your own recipes.
- Instance shutdown timeout – Specifies how long (in seconds) OpsWorks Stacks waits after triggering a Shutdown lifecycle event before stopping or terminating the EC2 instance. The default setting is 120 seconds.
Auto Healing
- All instances have OpsWorks Stacks agent to communicate regularly with AWS service.
- Stacks uses the communication for instance health monitoring.
- If no communication for > 5 minutes, instance is considered as failed.
- With auto healing Stacks replaces the layer’s
failed instances automatically
- If volume attached to instance and instance failed, the volume and its data are saved and attached to new instance.
- If volume not attached Stacks creates a new, empty volume with configuration specified by the layer, and attaches that volume to the new instance.
- By default auto healing is enabled in AWS OpsWorks
- Auto healing is set at layer level
Elastic Load Balancing Layer
- Using ELB
- Use the ELB console or API to create a load balancer
- then attach it to a presentation layer.
- ELB function is to
- Distributing traffic to layer’s instances
- Detect unhealthy EC2 instances
- Reroutes traffic to healthy instances
- Scales request handling capacity as per incoming traffic.
- Must create separate ELB load balancer for each layer in each stack needing balancing
- Assign a distinctive name to each ELB load balancer to use
RDS Service Layer
- It represents an RDS instance.
- Can represent only existing RDS instances
- Create RDS instances by RDS console or API.
ECS Cluster Layers
- ECS manages Docker containers on EC2 instances
- An ECS Cluster layer provides
- represents an Amazon ECS cluster
- Streamlined container instance provisioning and management
- Container instance operating system and package updates
- User permissions management
- Container instance performance monitoring
- EBS volume management
- Public and Elastic IP address management
- Security group management
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Free Practice TestTake a Quiz
