Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing–
- Make use of the internet
- Maintain data and application in remote servers to be accessed by users across the globe.
- on-demand delivery of IT resources and applications
- using the Internet
- pay-as-you-go pricing
Hence, it uses the computer resources that are delivered as a service over the internet.
Cloud Service Models
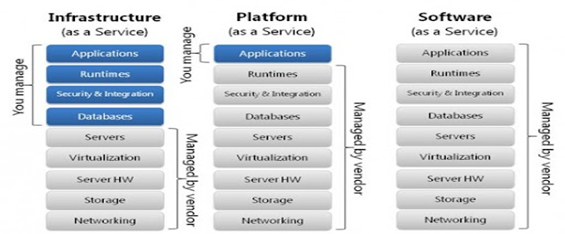
Various cloud service models are
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) –
- User accesses the physical hardware and can select as per need – CPU/storage/ etc.
- Resource availability is managed by IaaS cloud providers.
- Examples: Amazon CloudFormation, Rackspace Cloud, Google Compute Engine.
- User installs operating system images with required application software.
- Software patching and maintenance is responsibility of the user.
- Virtual machines (VMs) run as guests by a hypervisor, like Xen or KVM with operating system, middleware, network, storage, data and applications.
- IaaS payment depends upon resources subscribed, time used (per hour), usage of bandwidth (in gigabyte), storage(in gigabyte) or combination of any.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) –
- Complete development platforms with development tool is provided
- Developer builds applications without installing any tools on their computer and then deploy those applications without any specialized systems administration skills.
- The computer and storage resources scale automatically to match application demand in PaaS.
Examples of PaaS include
- App Engine from Google: based on Python and Django
- Force.com from SalesForce: based on the SalesForce SaaS infrastructure and Apex language
- Long Jump: based on Java/Eclipse
Software as a Service –
- Application software hosted in cloud, catering to user’s need is provided on subscription basis
- Application is accessed via web browser by users.
- Various business applications are provided – collaboration, CRM, ERP, invoicing, HRM, etc
- Reduces IT costs as less hardware and software maintenance costs.
- SaaS applications provide application customization.
- Users not responsible for hardware or software updates
- Example – Google Apps, Dropbox, Salesforce
Cloud Types
Various cloud type offerings depending upon level of control, are
Cloud Deployment Models
- All-in Cloud Based Deployment – Application is fully deployed in the cloud, with all components of the application running in the cloud.
- Hybrid Deployment – most common approach chosen and it connects infrastructure and applications between cloud-based resources and existing resources in data center.
AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Free Practice TestTake a Quiz
