Introduction to AWS Databases
Relational
- Relational databases store data with pre-defined schema
- relationships between them are defined
- designed for supporting ACID transactions
- maintaining referential integrity
- maintain data consistency
- Used for
- Traditional applications
- ERP
- CRM
- e-commerce
- AWS Offerings
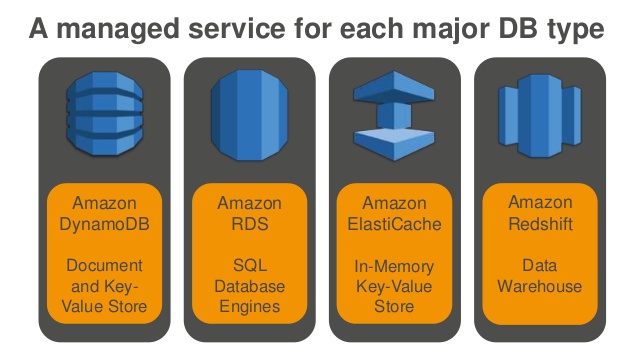
- Amazon Aurora
- MySQL, PostgreSQL
- Amazon RDS
- MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, SQL Server
- Amazon Redshift
Key-value databses
- Optimized to store and retrieve key-value pairs
- large data volumes with milliseconds retrieval
- without the performance overhead
- scale limitations of relational databases
- Used for
- Internet-scale applications
- real-time bidding
- shopping carts
- customer preferences
- AWS Offering
- Amazon DynamoDB
Document Databases
- Designed to store semi-structured data
- Stores documents
- Data is typically represented as a readable document
- Used for
- Content management
- Personalization
- mobile applications
- AWS Offering
- Amazon DocumentDB (with MongoDB compatibility)
In-memory Databases
- Used for applications that require real time access to data.
- By storing data directly in memory, microsecond latency is provided
- Used for
- Caching
- gaming leaderboards
- real-time analytics
- AWS Offerings:
- Amazon ElastiCache for Redis
- Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached
Graph Databases
- Used for applications needing to query and navigate relationships between highly connected, graph datasets with millisecond latency.
- Used for
- Fraud detection
- social networking
- recommendation engines
- AWS Offering
- Amazon Neptune
Time Series Databases
- Used to efficiently
- Collect
- Synthesize
- derive insights from enormous amounts of data
that changes over time (known as time-series data)
- Used for
- IoT applications
- DevOps
- industrial telemetry
- AWS Offering:
- Amazon Timestream
Ledger Databases
- Used for a centralized, trusted authority to maintain a scalable, complete and cryptographically verifiable record of transactions.
- Used for
- Systems of record
- supply chain
- registrations
- banking transactions
- AWS Offering:
- Amazon Quantum Ledger Database (QLDB)
Are you an AWS SysOps Administrator Associate?Take a Quiz
