Elasticity & Scalability
Elasticity
- Allows you to match the supply of resources—which cost money—to demand.
- Matching needs to utilization is critical for cost optimization.
- Demand includes
- external usage – number of customers visit website
- internal usage – application team using development and test environments.
- Two types
- Time-based elasticity – turning off resources when they are not being used
- Volume-based elasticity – matching scale to the intensity of demand,
Automating Time-Based Elasticity By
- The AWS Instance Scheduler can create automatic start and stop schedules for EC2 instance, using AWS CloudFormation template
- Terminate instances programmatically using Amazon EC2 APIs
- AWS Lambda functions can also shut down instances when, not being used.
- AWS Data Pipeline, web service to process and move data between AWS services
- Amazon CloudWatch, a monitoring service for AWS resources. It collects and tracks metrics and log files, set alarms, and automatically react to changes in AWS resources
Automating Volume-Based Elasticity By
- Amazon ECS – It can adjust its desired count up or down in response to CloudWatch alarms.
- Amazon EC2 Spot Fleets – A Spot Fleet can either launch instances (scale out) or terminate instances (scale in), within the chosen range, in response to one or more scaling policies.
- Amazon EMR clusters – Programmatically scale out and scale in core and task nodes in a cluster based on specified rules as per scaling policy.
- Amazon DynamoDB – Dynamically adjust provisioned throughput capacity in response to actual traffic patterns.
Scalability
- is the ability to quickly and easily increase or decrease the resources
- It affects resources for
- compute
- storage
- Auto Scaling is enabled by Amazon CloudWatch at no extra cost.
- Components
- Groups – logical groups containing collection of EC2 instances with similar characteristics for scaling and management purpose.
- Launch
Configuration – template used by auto scaling group to launch EC2 instances.
can specify
- the AMI
- instances type
- key pair
- security groups
- Scaling Plans – tells Auto Scaling when and how to scale.
- Scaling Types
- Manual scaling – specify only the changes in maximum, minimum, or desired capacity of your auto scaling groups.
- Auto-scaling maintains the instances with updated capacity.
- Scaling based on
- Schedule or time based
- demand
- Types of Scaling polices:-
- Target tracking scaling:- Based on the target value for a specific metric.
- Step scaling:- Based on a set of scaling adjustments that vary based on size of alarm breach.
- Simple scaling:- Based on a single scaling adjustment.
Auto Scaling Limits
Default Limits
- Launch configurations per Region: 200
- Auto Scaling groups per Region: 200
Auto Scaling Group Limits
- Scaling policies per Auto Scaling group: 50
- Scheduled actions per Auto Scaling group: 125
- Lifecycle hooks per Auto Scaling group: 50
- SNS topics per Auto Scaling group: 10
- Classic Load Balancers per Auto Scaling group: 50
- Target groups per Auto Scaling group: 50
Scaling Policy Limits
- Step adjustments per scaling policy: 20
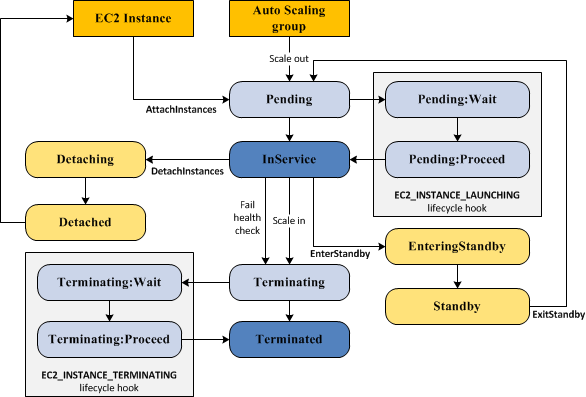
Auto Scaling Lifecycle
Are you an AWS SysOps Administrator Associate?Take a Quiz
