Cloud Bigtable Architecture Google Professional Data Engineer GCP
- Data is stored as a sorted map structure.
- Data is indexed at the column level as a group of
- row key
- a column key
- and a timestamp
- The index is the key mapping to the column’s actual value.
- Timestamp is for versioning.
- Data operations are conducted on a per-row basis so, all columns of a row are updated simultaneously.
- Automatic data compression is also done as applicable.
- Bigtable cluster may only operate within a single zone.
- For higher availability, configure with two separate clusters, each in a different zone of the same region.
Cloud Bigtable Architecture:
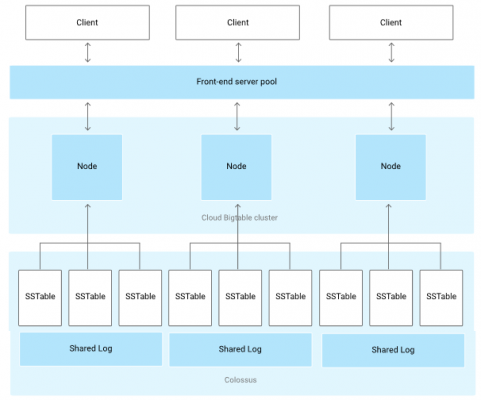
- Client requests go through a front-end server
- Nodes are organized into a Cloud Bigtable cluster of a Cloud Bigtable instance
- Each node in the cluster handles a subset of the requests to the cluster.
- Add nodes to increase the number of simultaneous requests to handle and maximum throughput
- Table is sharded into blocks of contiguous rows, called tablets similar to HBase regions. Tablets are stored on Colossus, Google’s file system, in SSTable format.
- An SSTable is a ordered immutable map from keys to values, and both are byte strings.
- Tablet is associated with a specific node.
- Writes are stored in Colossus’s shared log as acknowledged
- Data is never stored in nodes themselves;
- Node have pointers to a set of tablets stored on Colossus.
- Rebalancing tablets from one node to another is very fast
- Recovery from the failure of a node is very fast
- When a Cloud Bigtable node fails, no data is lost.
Google Professional Data Engineer (GCP) Free Practice TestTake a Quiz
