CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional Practice Exam

The Information Systems Security Architecture Professional (ISSAP) is a CISSP who specializes in designing security solutions and providing management with risk-based guidance to meet organizational goals. CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional facilitates the alignment of security solutions within the organizational context (e.g., vision, mission, strategy, policies, requirements, change, and external factors).
The CISSP-ISSAP is an appropriate credential if the candidate is a chief security architect or analyst. Typically, the candidate works as an independent consultant or in a similar capacity. As the architect, candidates play a key role in the information security department. Their responsibilities fall between the C-suite and upper managerial levels and the implementation of the security program. Although the role is tied closely to technology, it may be closer to the consultative and analytical process of information security.
Experience Requirements
Candidates must be a CISSP in good standing and have two years of cumulative paid work experience in one or more of the six domains of the CISSP-ISSAP CBK. You can learn more about CISSP-ISSAP experience requirements and how to account for part-time work and internships at www.isc2.org/Certifications/CISSPISSAP/experience-requirements.
CISSP-ISSAP Exam Format
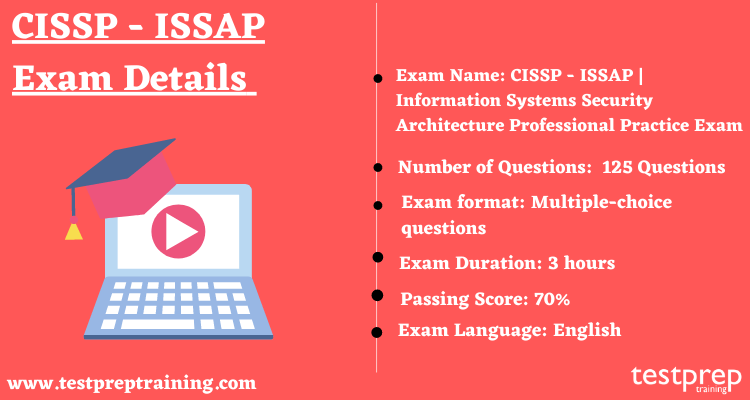
Explaining the format of CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional Practice Exam is the most important step. The exam includes 125 questions. The questions will appear in the form of multiple-choice. The candidate will get 3 hours to complete the exam. The CISSP-ISSAP Exam Questions are available in the English language. The passing score for CISSP – ISSAP is 700 (on a scale of 1-1000). CISSP ISSAP Exam Cost is $599 USD.
Scheduling: Pearson VUE
- Firstly, create an account with Pearson VUE, the exclusive global administrator of all (ISC)² exams.
- Secondly, select the (ISC)² certification exam you are pursuing.
- Thirdly, schedule your exam and testing location with Pearson VUE.
CISSP-ISSAP Exam Outline
The broad spectrum of topics included in the ISSAP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK®) ensures its relevancy across all disciplines in the field of information security. So, it is important to go through the whole course outline once and to understand and learn all the objectives. Below is the course outline for the CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional Practice Exam.
Domain 1: Architect for Governance, Compliance, and Risk Management 17%
Determine legal, regulatory, organizational, and industry requirements
- Determine applicable information security standards and guidelines
- Identify third-party and contractual obligations (e.g., supply chain, outsourcing, partners)
- Determine applicable sensitive/personal data standards, guidelines and privacy regulations
- Design for auditability (e.g., determine regulatory, legislative, forensic requirements, segregation, high assurance systems)
- Coordinate with external entities (e.g., law enforcement, public relations, independent assessor
Manage Risk
- Identify and classify risks
- Assess risk
- Recommend risk treatment (e.g., mitigate, transfer, accept, avoid)
- Risk monitoring and reporting
Security Architecture Modeling 15%
Identify security architecture approach
- Types and scope (e.g., enterprise, network, Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA), cloud, Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Control Systems (ICS)/Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA))
- Frameworks (e.g., Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture (SABSA), Service-Oriented Modeling Framework (SOMF))
- Reference architectures and blueprints
- Security configuration (e.g., baselines, benchmarks, profiles)
- Network configuration (e.g., physical, logical, high availability, segmentation, zones)
Verify and validate design (e.g., Functional Acceptance Testing (FAT), regression)
- Validate results of threat modeling (e.g., threat vectors, impact, probability)
- Identify gaps and alternative solutions
- Independent Verification and Validation (IV&V) (e.g., tabletop exercises, modeling and simulation, manual review of functions
Domain 3: Infrastructure Security Architecture 21%
Develop infrastructure security requirements
- On-premise, cloud-based, hybrid
- Internet of Things (IoT), zero trust
Design defense-in-depth architecture
- Management networks
- Industrial Control Systems (ICS) security
- Network security
- Operating systems (OS) security
- Database security
- Container security
- Cloud workload security
- Firmware security
- User security awareness considerations
Secure shared services (e.g., wireless, e-mail, Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), Unified Communications (UC), Domain Name System (DNS), Network Time Protocol (NTP))
Integrate technical security controls
- Design boundary protection (e.g., firewalls, Virtual Private Network (VPN), airgaps, software defined perimeters, wireless, cloud-native)
- Secure device management (e.g., Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), mobile, server, endpoint, cloud instance, storage)
Design and integrate infrastructure monitoring
- Network visibility (e.g., sensor placement, time reconciliation, span of control, record compatibility)
- Active/Passive collection solutions (e.g., span port, port mirroring, tap, inline, flow logs)
- Security analytics (e.g., Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), log collection, machine learning, User Behavior Analytics (UBA))
Design infrastructure cryptographic solutions
- Determine cryptographic design considerations and constraints
- Determine cryptographic implementation (e.g., in-transit, in-use, at-rest)
- Plan key management lifecycle (e.g., generation, storage, distribution)
Design secure network and communication infrastructure (e.g., Virtual Private Network (VPN), Internet Protocol Security (IPsec), Transport Layer Security (TLS))
Evaluate physical and environmental security requirements
- Map physical security requirements to organizational needs (e.g., perimeter protection and internal zoning, fire suppression)
- Validate physical security controls
Domain 4: Identity and Access Management (IAM) Architecture 16%
Design identity management and lifecycle
- Establish and verify identity
- Assign identifiers (e.g., to users, services, processes, devices)
- Identity provisioning and de-provisioning
- Define trust relationships (e.g., federated, standalone)
- Define authentication methods (e.g., Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), risk-based, location-based, knowledge-based, object-based, characteristics based)
- Authentication protocols and technologies (e.g., Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML), Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS), Kerberos
Design access control management and lifecycle
- Access control concepts and principles (e.g., discretionary/mandatory, segregation/Separation of Duties (SoD), least privilege)
- Access control configurations (e.g., physical, logical, administrative)
- Authorization process and workflow (e.g., governance, issuance, periodic review, revocation)
- Roles, rights, and responsibilities related to system, application, and data access control (e.g., groups, Digital Rights Management (DRM), trust relationships)
- Management of privileged accounts
- Authorization (e.g., Single Sign-On (SSO), rulebased, role-based, attribute- based)
Design identity and access solutions
- » Access control protocols and technologies (e.g., eXtensible Access Control Markup Language (XACML), Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP))
- Credential management technologies (e.g., password management, certificates, smart cards)
- Centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM) architecture (e.g., cloud-based, on-premise, hybrid)
- Decentralized Identity and Access Management (IAM) architecture (e.g., cloud-based, on-premise, hybrid)
- Privileged Access Management (PAM) implementation (for users with elevated privileges)
- Accounting (e.g., logging, tracking, auditing)
Domain 5: Architect for Application Security 13%
Integrate Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) with application security architecture (e.g., Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM), security architecture documentation, secure coding)
- Assess code review methodology (e.g., dynamic, manual, static)
- Assess the need for application protection (e.g., Web Application Firewall (WAF), anti-malware, secure Application Programming Interface (API), secure Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML))
- »etermine encryption requirements (e.g., at-rest, in-transit, in-use)
- Assess the need for secure communications between applications and databases or other endpoints
- Leverage secure code repository
Determine application security capability requirements and strategy (e.g., open-source, Cloud Service Providers (CSP), Software as a Service (SaaS)/Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)/ Platform as a Service (PaaS) environments)
- Review security of applications (e.g., custom, Commercial Off-the-Shelf (COTS), in-house, cloud)
- Determine application cryptographic solutions (e.g., cryptographic Application Programming Interface (API), Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG), key management)
- Evaluate applicability of security controls for system components (e.g., mobile and web client applications; proxy, application, and database services)
Identify common proactive controls for applications (e.g., Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP))
Domain 6: Security Operations Architecture 18%
Gather security operations requirements (e.g., legal, compliance, organizational, and business requirements)
Design information security monitoring (e.g., Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), insider threat, threat intelligence, user behavior analytics, Incident Response (IR) procedures)
- Detection and analysis
- Proactive and automated security monitoring and remediation (e.g., vulnerability management, compliance audit, penetration testing)
Design Business Continuity (BC) and resiliency solutions
- Incorporate Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
- Determine recovery and survivability strategy
- Identify continuity and availability solutions (e.g., cold, warm, hot, cloud backup)
- Define processing agreement requirements (e.g., provider, reciprocal, mutual, cloud, virtualization)
- Establish Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO)
- Design secure contingency communication for operations (e.g., backup communication channels, Out-of-Band (OOB))
Validate Business Continuity Plan (BCP)/Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) architecture
Design Incident Response (IR) management
- Preparation (e.g., communication plan, Incident
- Response Plan (IRP), training)
- Identification
- Containment
- Eradication
- Recovery
- Review lessons learned
CISSP – ISSAP FAQ
Examination Policies and Procedures
(ISC)² recommends that ISSAP candidates review exam policies and procedures prior to registering for the examination. Read the comprehensive breakdown of this important information at www.isc2.org/Register-for-Exam.
Recertification of the Exam
CISSP – ISSAP certification like every other certification requires maintenance. To clarify, CISSP – ISSAP certification requires to be recertified in order to maintain its status. You can recertify the exam if you’ve become decertified due to:
- Firstly, not meeting your required number of continuing professional education credits.
- Secondly, having the time limit on your endorsement expires.
Reschedule the Exam
You can reschedule your CISSP – ISSAP exam if you failed to take it on the scheduled date and time. In order to reschedule or cancel your exam appointment, contact Pearson VUE:
- Online at least 48 hours before the exam
- By phone at least 24 hours before the exam
Above all, Pearson VUE charges a reschedule fee of USD$50 and a cancellation fee of USD$100.
Preparation Guide to qualify CISSP – ISSAP
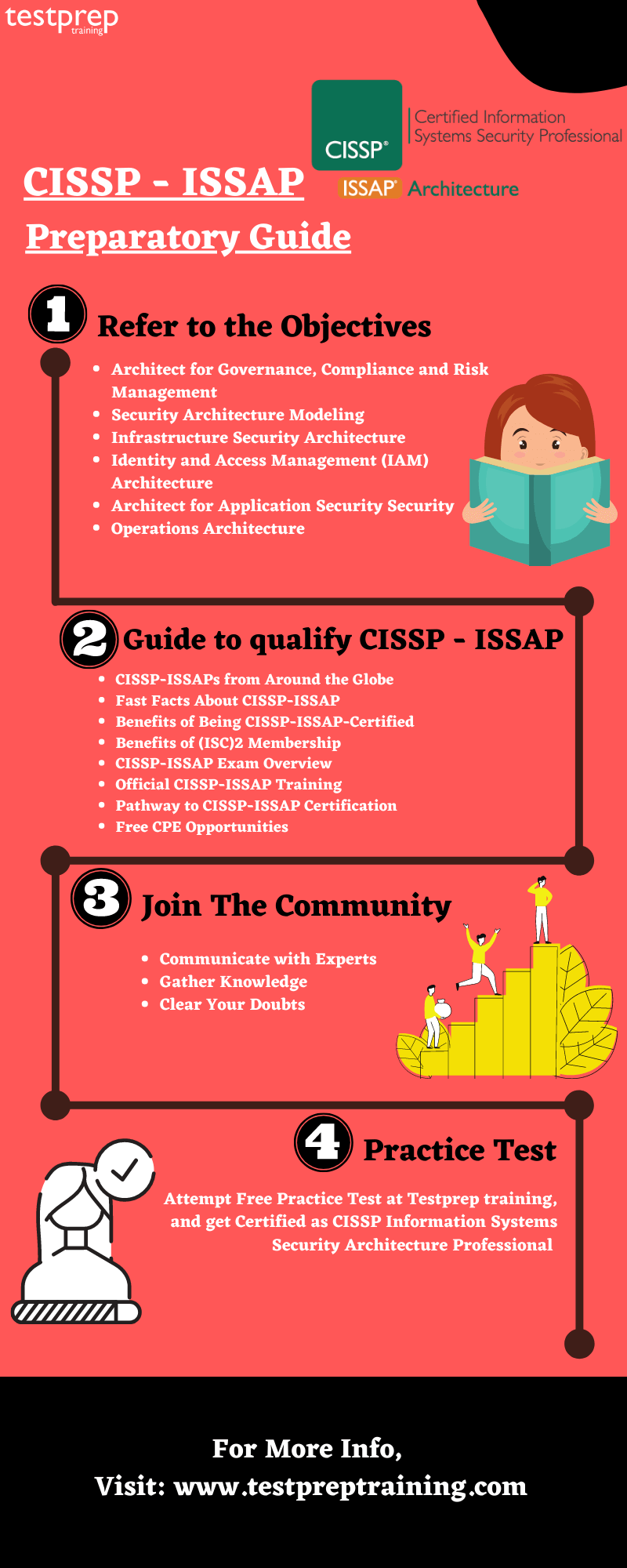
To start the ideal preparation for the CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional Practice Exam, the following details a few of the analytical steps that you should consider for developing an ideal schedule for your CISSP-ISSAP Exam Preparation.
(ISC)² Official Website
First of all, you should visit the official website of (ISC)² because it offers the most reliable information about the exam. (ISC)² provides a CISSP-ISSAP Study Guide for each of its certifications and exams. The CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional Practice Exam content is also present on the (ISC)² website such as relevancy across all disciplines in the field of information security relevancy across all disciplines in the field of information security. It also includes the objectives and the basic details about the exam.
Review all the Exam Objectives
Your first step in the CISSP-ISSAP Exam Guide is to review all the exam objectives. And, to do so, make sure to visit the Official Website of CISSP – ISSAP exam. As this is the most authentic site for obvious reasons. By doing so, you’ll have a clear view of each and every information related to the CISSP – ISSAP exam. So, make sure, to begin with, this step.
- Architect for Governance, Compliance and Risk Management
- Security Architecture Modeling
- Infrastructure Security Architecture
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Architecture
- Architect for Application Security
- Security Operations Architecture
Download Exam skill Outline
After this, you must download the exam skill outline available on the official website itself. Downloading the outline will provide you with the updated exam outline. All the domains and their subtopics are listed down in the outline. Keep in mind not to rely on any other website except the official website itself. Since the exam is updated after every few years hence the official website is your door to reliable information.
Official (ISC)² Guide to the CISSP – ISSAP
The Official (ISC)² Guide to the CISSP – ISSAP supplies an authoritative review of the key concepts and requirements of the CISSP – ISSAP. This guide encompasses verything to know about this elite and specialized certification. See how the CISSP-ISSAP concentration builds on the CISSP and helps you design the next level of your career.
Online Self-Paced Training
Official (ISC)² Online Self-Paced Training gives you the freedom and confidence to move ahead on your schedule. Throughout the entire learning experience, you have on-demand access to recorded video content from an (ISC)² Authorized Instructor – a subject matter expert who holds the credential you’re pursuing. Course activities draw from real-world scenarios and industry topics to reinforce the material and increase your knowledge retention.
Join a Study Group
For passing the CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional Practice Exam, the candidate needs to get and share knowledge. So, we are suggesting you join some study where you can discuss the concepts with the people who have the same goal. This will lead the candidate throughout their preparation.
CISSP-ISSAP Practice Tests
The most important step is to try your hands on the practice test. Practice tests are the one which ensures the candidate about their preparation. There are many CISSP-ISSAP Practice Exams available on the internet nowadays, the candidate can choose whichever they want. The practice test is very beneficial in preparing for the CISSP – ISSAP | Information Systems Security Architecture Professional Practice Exam. So, Start Preparing Now!